Obesity, Weight, and Cancer Risk
Many
factors cause people to become overweight or obese, including genetic,
hormonal, environmental, emotional, and cultural factors. More than two-thirds
of American adults are overweight and obese. This means that they have too much
body fat compared to lean body tissue, such as muscle.
Ø Which cancers are affected?
·
Overweight
or obese have a higher risk of many serious health conditions
·
Including type-2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and
heart disease. Increased levels of insulin and insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1),
which may help some cancers develop
·
Being
overweight or obese is also associated with an increased risk of cancer.
·
Chronic, low-level inflammation, which is more common
in people who are obese and is linked with an increased cancer risk
·
Higher amounts of estrogen produced by fat tissue,
which can drive the development of some cancers, such as breast and endometrial
cancers
·
Obesity
now linked to 12 different cancers
ü The
following factors can affect your cancer risk:
- Gaining
weight as an adult
- Losing
and regaining weight repeatedly
- Fat
cells may also effect processes that regulate cancer cell growth.
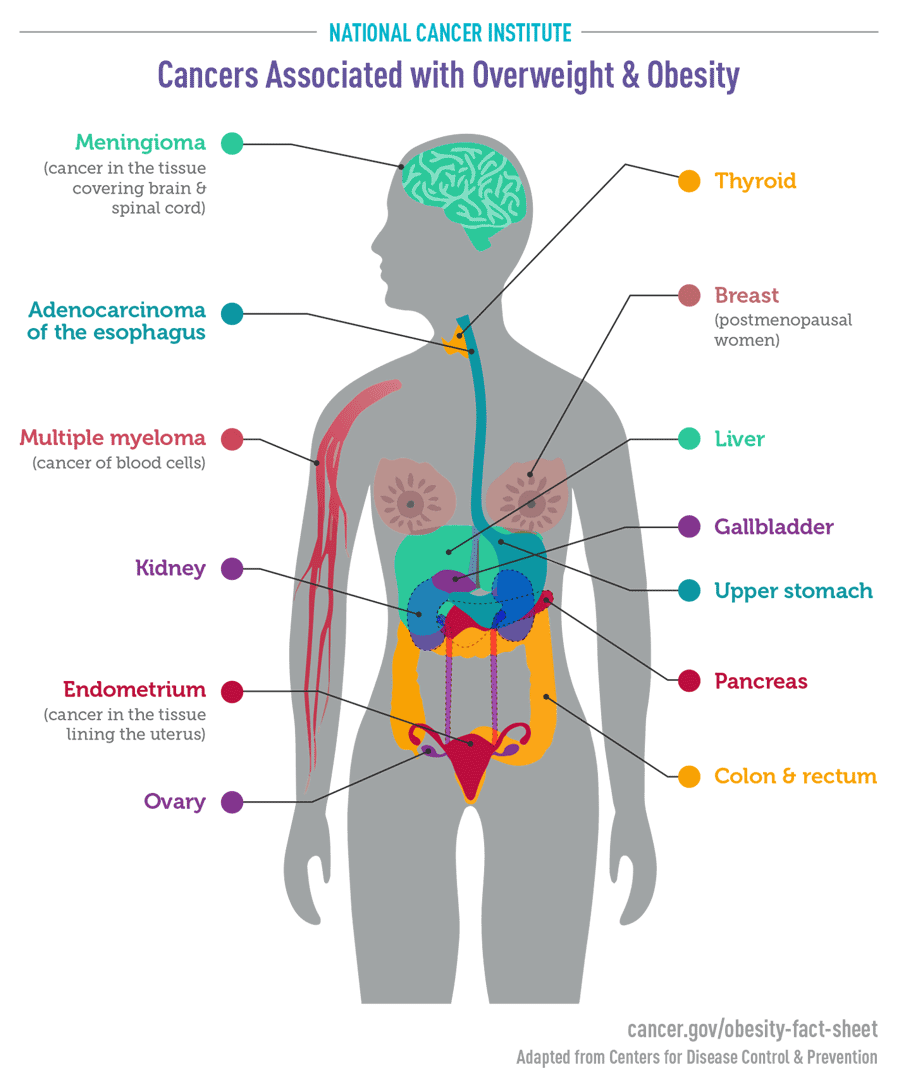
ü Types of cancer linked to
overweight or obesity
Being overweight or obese has
been linked to some cancers:
v Breast
v Colorectal
v Uterine
v Kidney
v Head and neck
v Esophageal
v Pancreatic
v Endometrium (lining of the
uterus)
v Prostate
v Gallbladder
v Thyroid
ü Measuring weight gain
A normal
BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9. A BMI between 25 and 29.5 is considered
overweight, while a BMI of 30 or higher is obese. In addition, people with
larger waist measurements have a higher risk of various diseases, such as heart
disease. A normal waist measurement is under 40 inches for men and under 35
inches for women.
ü Weight manage tips
v
Eat more
vegetables, fruits, lean protein, and whole grains. Some types of food, such as
broth-based soups, also help a person feel "full" faster.
v
Limit
foods and beverages that are high in sugar, such as juice and soda.
v
Eat and
drink only as many calories as you need to maintain a healthy weight and
support your level of physical activity.
v
Aim for
30 to 60 minutes per day of moderate to intense physical activity on most days.
But even a small increase in physical activity has benefits.
v
A change
in lifestyle behaviors.
v
A change
in lifestyle behaviors.
v
Behavior
change support
v
Medications.
v
Surgery
Note:-A healthy body weight is important for children as well as adults
ü One in five children
are overweight or obese before they begin primary school, and one in three
children are overweight or obese by the time they leave.
ü One of every five
youngsters are overweight or fat before they start grade school, and one of
every three kids are overweight or stout when they clear out.
ü Obese kids will
probably develop into stout grown-ups, and hefty grown-ups are more in danger
of disease. It is conceivable overweight kids might be at expanded danger of
cancer as grown-ups, paying little heed to what they grow up to weigh, however
the proof isn't clear.
ü By encouraging your
kids to lead a sound way of life, you can enable them to keep a well body
weight as a kid and also later on throughout everyday life.






